Django Production Deployment on Apache Server
Building an software application using different algorithms, data-structures, frameworks, databases and messaging queues which can solve the mentioned problem efficiently and effectively. This is the first part of solving the problem. The second part is to deploy and maintain the application for high scalability and availability. This is as important as developing algorithms and building software applications.
To understand it's importance assume you have an application like imdb which will provide information related to movies, actors and their works. The expected workload on average could be 1000 requests per second with 300ms serving time for each request. The numbers are not quite high for some SQL db based application right? But without proper configuration applications will not be able serve even 100 request per second. Are you thinking we can increase just the number of servers to server more request as cloud providers allows to scale very quickly. Don't do that, it's possible that you will spend more money than you will generate.
The correct configuration to maximize the throughput of application is not just limited to properly configuring web-servers but also databases, messaging queues and other components of the entire application. In this article we will focus on how we can configure Django application on Apache web-server on Unix based operating system to maximize the output. We will not talk about why should we use an server to host our applications. I would recommend you to search about it on your own.
Before looking at final configuration let's understand few terms and about application
- mod_wsgi: It provides an Apache module based on the python WSGI specification. WSGI standard helps to setup an standard interface between web-servers and web-frameworks. The idea behind WSGI to have server and application. server will invoke your application. There could be some "middleware" too which helps both side to communicate with each other. I would recommend to read WSGI specification to understand more about it. mod_wsgi allows to deploy code for frameworks like like Django, Flask, Pyramid and etc
-
Movie App: We have built an Django application named imdb. This is an simple application which returns a list of movies already populated into the SQLite DB. We will not deep dive into the how rest APIs can be built into Django app. We have already exposed an API
/moviewhich will return list of movies.
Let's look at the
wsgi.pypresent insideimdb/imdbfolder. wsgi.py file is entry-point for modwsgi to call the application. Later in article we will see how we provide entry-point for our application to Apache module of modwsgi. There is a small change we have done so that theimdbapp will have it's own process. We will deep dive further into this later in the article.
"""
WSGI config for imdb project.
It exposes the WSGI callable as a module-level variable named ``application``.
For more information on this file, see
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.1/howto/deployment/wsgi/
"""
import os
from django.core.wsgi import get_wsgi_application
# comment and add new line so the process deamon will not be shared between multiple applications
# os.environ.setdefault('DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE', 'imdb.settings')
os.environ["DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE"] = "imdb.settings"
application = get_wsgi_application()Django app will have line number 14 by default, which will cause app to share the process with other applications hosted by modwsgi in the same machine. By commenting line number 14 and adding line number 15, we are instructing modwsgi to use separate process for this application.
Apache allows to host applications in three ways Embedded, Daemon and Event mode. We will only talk about first two in the this article.
Embedded Mode: This mode is also known as prefork mode, this is implemented by Apache MPM prefork module. This is the default mode for the Apache server. In this mode both the proxy and the response processes are being managed by Apache only which is why it's called embedded mode. This mode is suitable for non-threaded applications or libraries. Here process are the ones which serve the request. Each process is isolated from another process. So even if there is an issue with one process, another will not be affected due to it.
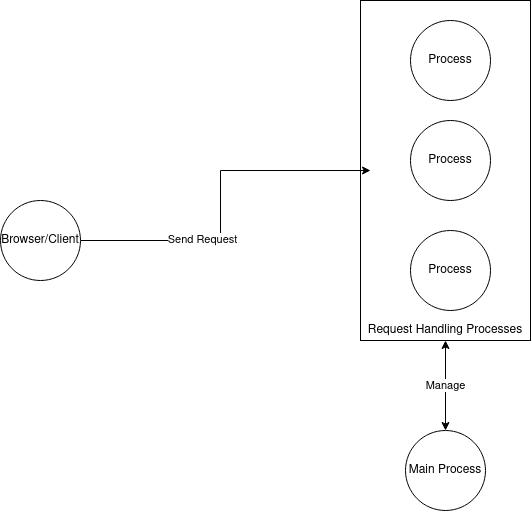
As we can see in the diagram the main Apache process manages the process which will serve the request. So in this case a lot of processes will get created and killed which will take substantial amount of CPU in managing these process. As a separate memory need to be allocated and releases for each process. Let's discuss about the configuration shown below
-
Virtual Host: This is the block where we mention the application entry-point to mod_wsgi. All the settings shown inside virtual host will be common for daemon and embedded mode. In case of daemon mode there will be few additional settings
- ServerName: It can be the domain name by which we want to access the application or it can be the IP address of the server
- WSGIScriptAlias: It is used to specify physical path of the wsgi script for the given application
- WSGIApplicationGroup: It is used to group the applications hosted in single server. If there are multiple applications hosted in, we can group them to use the same python sub interpreter. If there is single application you can set it %{GLOBAL}
- Directory-Files: This makes sure that Apache can access wsgi.py file
- WSGIPythonPath: This allows wsgi to search python modules. As Django application is built of modules and wsgi.py shown above tries to access imdb module.
-
mpmpreforkmodule: Here we set the configuration for our server. As in embedded mode requests are served by process. So, we will look here what is the meaning of each directive
- StartServer: The number of server process which should be active by default when server starts. Be cautious of the number you set here. As each process is an copy of the application you want to run and each one of it will reserve memory for itself. So setting very high number will throw you out of memory and processes will compete with each other to get memory without serving any request.
- MinSpareServers: It represents the number of ideal process, who will be up and running but will not serve any request.
- MaxSpareServers: it represents the maximum number of ideal process, who will be up and running but will not serve any request
- ServerLimit: Be careful with this property and do not set it if you don't know what it can do for you. This lets you set maximum request serve can handle including requests in process and queue
- MaxConnectionsPerChild: This property is to define number of request which an processes will handle in it's lifetime before being killed. Never configure this property unless you know what you are doing, as keeping this number too less will just consume your memory and most of CPU time will get exhausted due to process churn.
<IfModule mpm_prefork_module>
StartServers 2
MinSpareServers 2
MaxSpareServers 6
MaxRequestWorkers 30
#ServerLimit
#MaxConnectionsPerChild 5
</IfModule>
WSGIPythonPath /var/www/imdb
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName localhost
WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/imdb/imdb/wsgi.py
WSGIApplicationGroup %{GLOBAL}
<Directory /var/www/imdb/imdb>
<Files wsgi.py>
Require all granted
</Files>
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>In case of embedded mode it's better to use default settings of Apache, until you are not an expert in Apache configuration and you understand working of Apache well. As in embedded mode process are created and killed frequently, it puts a lot of pressure on the system.
Daemon Mode: This is know as worker mode and implemented by mpmworkermodule. Worker mode implements a multi-process and multi-threaded approach to where the requests will be handled by threads instead of process. As the cost of creation and context switch for threads are quite less compared to process. We can refer the below diagram for better understanding
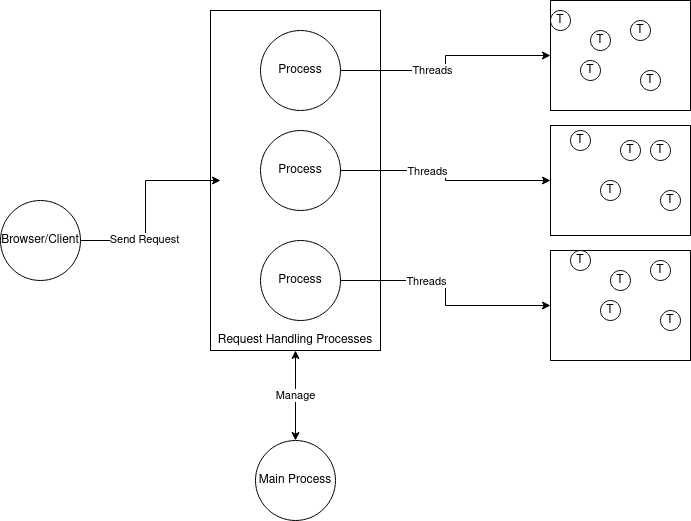
Here the parent process will maintain the worker process and worker processes will handle threads which will serve the request. Each request will be passed to thread. Here Apache will only work as proxy which will accept request and pass the request to one of the threads, hence reducing the wait time for users. Daemon mode configuration of Apache is more forgiving, as even if you have not done the configuration properly it will not consume all resources. Let's see an configuration sample for example
<IfModule mpm_worker_module>
ServerLimit 16
StartServers 2
MaxRequestWorkers 150
MinSpareThreads 25
MaxSpareThreads 75
ThreadsPerChild 25
</IfModule>
WSGIRestrictEmbedded On
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName localhost
WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/imdb/imdb/wsgi.py
WSGIDaemonProcess imdb python-path=/var/www/imdb processes=5 threads=15
WSGIProcessGroup imdb
WSGIApplicationGroup %{GLOBAL}
<Directory /var/www/imdb/imdb>
<Files wsgi.py>
Require all granted
</Files>
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>We will only talk about properties which we have not discussed
-
Virtual Host
- WSGIDaemonProcess: This directive enables the number of daemon process that should be created which will manage threads to serve the request as well as number of threads in each process which should be created.
- WSGIProcessGroup: This given an unique group name to the process created in daemon name. Both WSGIDaemonProcess and WSGIProcessGroup are must to enable daemon mode.
- WSGIRestrictEmbedded On: This directive forces to run applications in daemon mode only
-
mpmworkermodule
- MaxRequestWorkers: In Daemon mode it defines the no of request which can run simultaneously to server user request
- MinSpareThreads: Minimum number of threads that should be in ideal state to serve request
- MaxSpareThreads: Maximum number of threads that should be in ideal state at any given point of time to serve request
- ThreadsPerChild: The number of threads that can be managed by each process
In the above configuration we have defined major of settings in number threads such ThreadsPerChild. Apache will automatically allocate enough process based on these number.
Now we know How does embedded and Daemon mode actually works, but still there is a question which mode should we choose and exactly why?
- Apache is not designed specifically to server python applications, but mod_wsgi daemon process are designed only for python applications. So they will help us to achieve maximum out of python web applications.
- Embedded Mode uses processes to serve the request, but daemon mode uses threads to serve request. If you know about processes vs threads, you will know why using threads are better compared to process. It will save you a lot of memory, CPU for each request. You can utilize the resources at it's maximum.
- Embedded mode is useful if you are serving an rare case application where threading can't be applied, but same kind of setup can be achieved by configuration in daemon mode too.
- Any code change will need Apache server restart, but that is not the case for daemon mode. Restarting sever in where multiple applications are hosted in same server could be problematic.
So that was enough of theory let's see in working daemon and embedded mode config.
Embedded Mode
We have created an docker file named Dockerfile.embedded, which uses an alpine image to do the configuration. We can split them into multiple steps
- Use Alpine as base Image
- Install python, pip and Apache with mod_wsgi
- Move imdb_embedded.conf to Apache configuration directory. imdb_embedded.conf is the same config which we saw earlier. Install pip dependencies and move an httpd-foreground shell script to bin folder to make it available as command
- Expose port 80 on Docker container
- Run httpd-foreground command to start Apache server
FROM alpine:3.12.0
RUN apk --update --no-cache add python3=3.8.5-r0 python3-dev=3.8.5-r0 py3-pip=20.1.1-r0 apache2=2.4.46-r0 apache2-dev=2.4.46-r0 apache2-mod-wsgi=4.7.1-r0;\
ln -s python3 /usr/bin/python;
ADD . .
RUN cp -R imdb /var/www/;cp imdb_embedded.conf /etc/apache2/conf.d/imdb_embedded.conf; pip install -r requirements.txt; chmod +x httpd-foreground; cp httpd-foreground /usr/local/bin
EXPOSE 80
CMD ["httpd-foreground"]Run Docker file from the django-apache folder in your local docker build -f Dockerfile.embedded . to build docker image, which will return an image id once image is built, use imageid with the command `docker run -d -p 8000:80 imageid, This will run an container in your local and you can access the application on local port 8000 of your machine. Usecurl http://localhost:8000/movie` to access list of movies available in SQLite db.
Daemon Mode
There is another file name Dockerfile.daemon, which we can use to run application in daemon mode. Let's split the docker file in steps to understand what it does.
- Take Debian buster slim as base image
- Install Apache Python3, pip and mod_wsgi in to it
- Move imdb_daemon.conf to configuration directory. Disable event mode and enable worker mode. Install python dependencies
- Expose Port 80 of the container
- Use apache2ctl utility to start the web-server
FROM debian:buster-slim
RUN apt-get update; apt-get install -y python3 python3-dev python3-pip apache2 apache2-dev libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3;ln -s pip3 /usr/bin/pip; a2dismod mpm_event;\
a2enmod mpm_worker
# replace a2enmod mpm_worker with a2enmod mpm_prefork in above command for embedded mode
ADD . .
RUN cp -R imdb /var/www/imdb;cp imdb_daemon.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/imdb.conf; pip install -r requirements.txt; a2ensite imdb.conf; a2dissite 000-default.conf; rm /var/www/html/index.html
# replace imdb_deamon.conf with imdb_embedded.conf for embedded mode
EXPOSE 80
CMD ["apache2ctl", "-D", "FOREGROUND"]We can use the same steps as embedded docker file to run daemon mode docker file. Additionally we have included instructions to run application in embedded mode on Debian.
Let's end this post for now and we will see the difference in performance in some other post. You can find the source code for this post in following link.
Before we close the post, are you thinking why we are using Debian version instead of Alpine for Daemon mode?
Daemon mode does not works properly on Alpine Linux. The issue has been there for quite sometime. You can see following below links. Actually there is not much difference in the size of Alpine and Debian Slim buster container, it almost just 100 Mb.
- https://github.com/GrahamDumpleton/mod_wsgi/issues/455
- https://modwsgi.narkive.com/WAUhcjDB/wsgidaemonprocess-segfault-inside-docker-alpine-linux
To verify in which mode Apache server is running you can use apache2ctl -V in Debian or httpd -V Alpine.
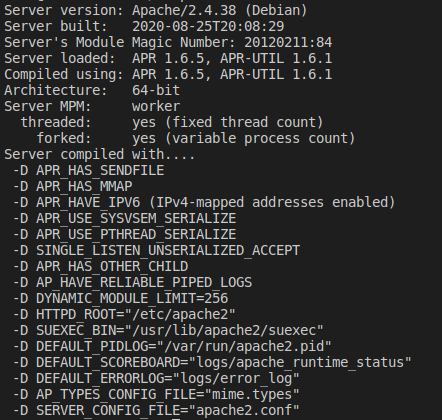
You can look at Server MPM section which will consist worker for Daemon mode and prefork for Embedded.